Scientists are getting closer to uncovering the origins of the first dinosaurs, with recent studies suggesting that these creatures may have lived in remote and challenging-to-reach areas for around 230 million years. The primary evidence points towards Gondwana, a region associated with Pangaea.
Summary of essential information to understand
- Dinosaurs first appeared more than 230 million years ago in Gondwana, as evidenced by ancient fossils.
- It is challenging to discover new records due to the conditions for fossilization in tropical regions.
- Researchers propose that significant findings could be concealed in areas like the Sahara and the Amazon.
Where did the dinosaurs originate from, ultimately?
Dinosaurs were spreading worldwide in ancient times, with a primary focus on Gondwana, which includes present-day Africa, South America, South Asia, Australia, and Antarctica. Other continents like Laurasia also exhibit some signs of dinosaur presence, though the evidence is less direct.
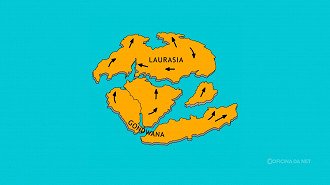
Fossils are scarce in equatorial regions like the Sahara and the Amazon due to the challenging conditions required for fossilization and limited access for paleontological research.
What are the findings of evolutionary research?
Fossil evidence and ancient planetary geography indicate that Gondwana was the original habitat of dinosaurs. Fossils of reptiles like silesaurids, potential ancestors of dinosaurs in the ornithic group, support this theory. Finding these creatures in regions now part of the Sahara and the Amazon may provide further insights into this narrative.
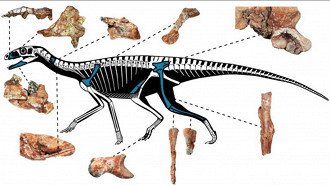
The potential for future discoveries in untapped areas is hopeful despite the obstacles. Science is focused on these regions where new fossils could revolutionize our understanding of the early stages of dinosaurs on Earth.